Leica D-LUX Typ 109 vs Sony A7R IV
The Leica D-LUX (Typ 109) and the Sony Alpha A7R IV are two enthusiast cameras that were revealed to the public, respectively, in September 2014 and July 2019. The D-LUX Typ 109 is a fixed lens compact, while the A7R IV is a mirrorless interchangeable lens camera. The cameras are based on a Four Thirds (D-LUX Typ 109) and a full frame (A7R IV) sensor. The Leica has a resolution of 12.7 megapixels, whereas the Sony provides 60.2 MP.
Below is an overview of the main specs of the two cameras as a starting point for the comparison.

Check D-LUX Typ 109 offers at
ebay.com

Check A7R IV offers at
ebay.com
Going beyond this snapshot of core features and characteristics, what are the differences between the Leica D-LUX (Typ 109) and the Sony Alpha A7R IV? Which one should you buy? Read on to find out how these two cameras compare with respect to their body size, their imaging sensors, their shooting features, their input-output connections, and their reception by expert reviewers.
Body comparison
The physical size and weight of the Leica D-LUX Typ 109 and the Sony A7R IV are illustrated in the side-by-side display below. The two cameras are presented according to their relative size. Three consecutive perspectives from the front, the top, and the back are available. All width, height and depth dimensions are rounded to the nearest millimeter.
The D-LUX Typ 109 can be obtained in two different colors (black, grey), while the A7R IV is only available in black.



If the front view area (width x height) of the cameras is taken as an aggregate measure of their size, the Sony A7R IV is considerably larger (59 percent) than the Leica D-LUX Typ 109. It is noteworthy in this context that the A7R IV is splash and dust-proof, while the D-LUX Typ 109 does not feature any corresponding weather-sealing.
The above size and weight comparisons are to some extent incomplete and possibly misleading, as the D-LUX Typ 109 has a lens built in, whereas the A7R IV is an interchangeable lens camera that requires a separate lens. Attaching the latter will add extra weight and bulk to the setup. You can compare the optics available for the A7R IV and their specifications in the Sony FE Lens Catalog.
Concerning battery life, the D-LUX Typ 109 gets 300 shots out of its Leica BP-DC15 battery, while the A7R IV can take 670 images on a single charge of its Sony NP-FZ100 power pack. The power pack in the A7R IV can be charged via the USB port, which can be very convenient when travelling.
The adjacent table lists the principal physical characteristics of the two cameras alongside a wider set of alternatives. If you want to switch the focus of the display and review another camera pair, you can move across to the CAM-parator tool and choose from the broad selection of possible camera comparisons there.

| # | Camera Model |
Camera Width |
Camera Height |
Camera Depth |
Camera Weight |
Battery Life |
Weather Sealing |
Camera Launch |
Launch Price (USD) |
Street Price |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Leica D-LUX Typ 109 | 118 mm | 66 mm | 55 mm | 405 g | 300 | n | Sep 2014 | 1,195 | ebay.com | |
| 2. | Sony A7R IV | 129 mm | 96 mm | 78 mm | 665 g | 670 | Y | Jul 2019 | 3,499 | ebay.com | |
| 3. | Canon G16 | 109 mm | 76 mm | 40 mm | 356 g | 360 | n | Aug 2013 | 549 | ebay.com | |
| 4. | Fujifilm X30 | 119 mm | 72 mm | 60 mm | 423 g | 470 | n | Aug 2014 | 599 | ebay.com | |
| 5. | Fujifilm X100T | 127 mm | 74 mm | 52 mm | 440 g | 330 | n | Sep 2014 | 1,299 | ebay.com | |
| 6. | Fujifilm X20 | 117 mm | 70 mm | 57 mm | 353 g | 270 | n | Jan 2013 | 599 | ebay.com | |
| 7. | Fujifilm X100S | 127 mm | 74 mm | 54 mm | 445 g | 330 | n | Jan 2013 | 1,299 | ebay.com | |
| 8. | Leica D-LUX 7 | 115 mm | 66 mm | 65 mm | 392 g | 300 | n | Nov 2018 | 1,195 | ebay.com | |
| 9. | Leica V-LUX Typ 114 | 137 mm | 99 mm | 131 mm | 830 g | 360 | n | Sep 2014 | 1,349 | ebay.com | |
| 10. | Leica X Typ 113 | 133 mm | 73 mm | 78 mm | 486 g | 350 | n | Sep 2014 | 2,295 | ebay.com | |
| 11. | Leica D-LUX 6 | 111 mm | 68 mm | 46 mm | 298 g | 330 | n | Sep 2012 | 699 | ebay.com | |
| 12. | Panasonic LX100 | 115 mm | 66 mm | 55 mm | 393 g | 300 | n | Sep 2014 | 899 | ebay.com | |
| 13. | Sony A7R IVA | 129 mm | 96 mm | 78 mm | 665 g | 670 | Y | Apr 2021 | 3,499 | amazon.com | |
| 14. | Sony A7S III | 127 mm | 97 mm | 81 mm | 699 g | 600 | Y | Jul 2020 | 3,499 | amazon.com | |
| 15. | Sony A9 II | 129 mm | 96 mm | 76 mm | 678 g | 690 | Y | Oct 2019 | 4,499 | amazon.com | |
| 16. | Sony A7 III | 127 mm | 96 mm | 74 mm | 650 g | 610 | Y | Feb 2018 | 1,999 | amazon.com | |
| 17. | Sony A7R III | 127 mm | 96 mm | 74 mm | 650 g | 650 | Y | Oct 2017 | 3,199 | ebay.com | |
| Note: Measurements and pricing do not include easily detachable parts, such as add-on or interchangeable lenses or optional viewfinders. | |||||||||||
Any camera decision will obviously take relative prices into account. The manufacturer’s suggested retail prices give an idea on the placement of the camera in the maker’s lineup and the broader market. The D-LUX Typ 109 was launched at a lower price than the A7R IV, despite having a lens built in. Usually, retail prices stay at first close to the launch price, but after several months, discounts become available. Later in the product cycle and, in particular, when the replacement model is about to appear, further discounting and stock clearance sales often push the camera price considerably down. Then, after the new model is out, very good deals can frequently be found on the pre-owned market.
Sensor comparison
The imaging sensor is at the core of digital cameras and its size is one of the main determining factors of image quality. All other things equal, a large sensor will have larger individual pixel-units that offer better low-light sensitivity, wider dynamic range, and richer color-depth than smaller pixels in a sensor of the same technological generation. Further, a large sensor camera will give the photographer additional creative options when using shallow depth-of-field to isolate a subject from its background. On the downside, larger sensors tend to be associated with larger, more expensive camera bodies and lenses.
Of the two cameras under consideration, the Leica D-LUX Typ 109 features a Four Thirds sensor and the Sony A7R IV a full frame sensor. The sensor area in the A7R IV is 359 percent bigger. As a result of these sensor size differences, the cameras have a format factor of, respectively, 2.0 and 1.0. The sensor in the D-LUX Typ 109 has a native 4:3 aspect ratio, while the one in the A7R IV offers a 3:2 aspect. The D-LUX Typ 109 has the particularity of featuring a switch that allows to toggle between multiple aspect ratios, while maintaining the same field of view and full image resolution.
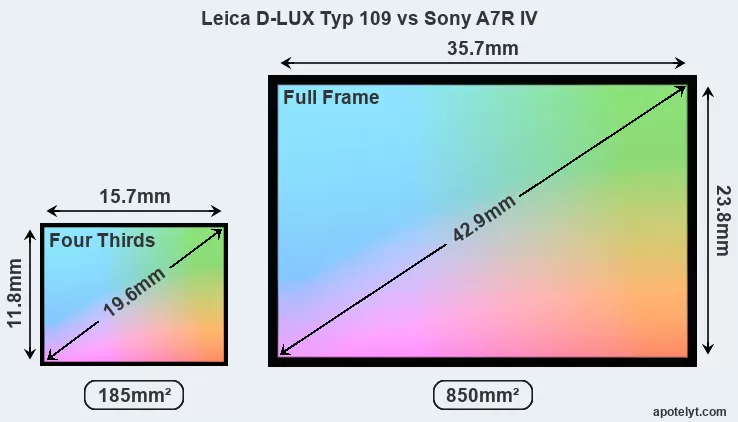
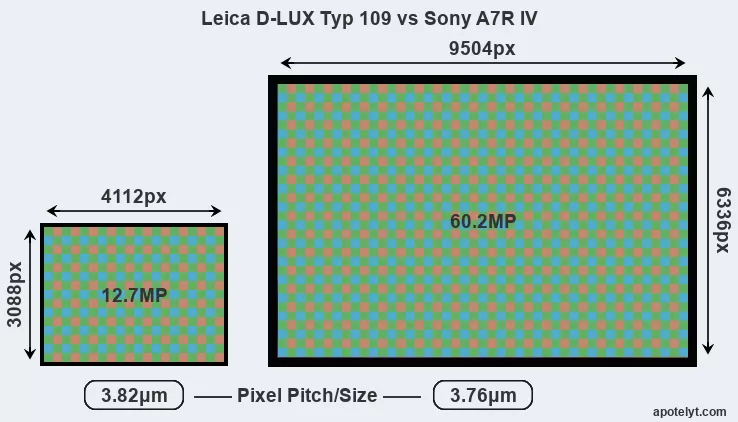
With 60.2MP, the A7R IV offers a higher resolution than the D-LUX Typ 109 (12.7MP), but the A7R IV has marginally smaller individual pixels (pixel pitch of 3.76μm versus 3.82μm for the D-LUX Typ 109). Yet, the A7R IV is a much more recent model (by 4 years and 10 months) than the D-LUX Typ 109, and its sensor will have benefitted from technological advances during this time that enhance the light gathering capacity of its pixel-units. Coming back to sensor resolution, it should be mentioned that the A7R IV has no anti-alias filter installed, so that it can capture all the detail its sensor resolves.
The resolution advantage of the Sony A7R IV implies greater flexibility for cropping images or the possibility to print larger pictures. The maximum print size of the A7R IV for good quality output (200 dots per inch) amounts to 47.5 x 31.7 inches or 120.7 x 80.5 cm, for very good quality (250 dpi) 38 x 25.3 inches or 96.6 x 64.4 cm, and for excellent quality (300 dpi) 31.7 x 21.1 inches or 80.5 x 53.6 cm. The corresponding values for the Leica D-LUX Typ 109 are 20.6 x 15.4 inches or 52.2 x 39.2 cm for good quality, 16.4 x 12.4 inches or 41.8 x 31.4 cm for very good quality, and 13.7 x 10.3 inches or 34.8 x 26.1 cm for excellent quality prints.
The A7R IV has on-sensor phase detect pixels, which results in fast and reliable autofocus acquisition even during live view operation.
Unlike the D-LUX Typ 109, the A7R IV has the capacity to capture high quality composite images (241MP) by combining multiple shots after shifting its sensor by miniscule distances. This multi-shot, pixel-shift mode is most suitable for photography of stationary objects (landscapes, studio scenes).
The Leica D-LUX (Typ 109) has a native sensitivity range from ISO 200 to ISO 12500, which can be extended to ISO 100-25600. The corresponding ISO settings for the Sony Alpha A7R IV are ISO 100 to ISO 32000, with the possibility to increase the ISO range to 50-102400.
In terms of underlying technology, the D-LUX Typ 109 is build around a CMOS sensor, while the A7R IV uses a BSI-CMOS imager. Both cameras use a Bayer filter for capturing RGB colors on a square grid of photosensors. This arrangement is found in most digital cameras.
For many cameras, data on sensor performance has been reported by DXO Mark. This service assesses and scores the color depth ("DXO Portrait"), dynamic range ("DXO Landscape"), and low-light sensitivity ("DXO Sports") of camera sensors, and also publishes an overall camera score. The following table provides an overview of the physical sensor characteristics, as well as the sensor quality measurements for a selection of comparators.

| # | Camera Model |
Sensor Class |
Resolution (MP) |
Horiz. Pixels |
Vert. Pixels |
Video Format |
DXO Portrait |
DXO Landscape |
DXO Sports |
DXO Overall |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Leica D-LUX Typ 109 | Four Thirds | 12.7 | 4112 | 3088 | 4K/30p | 22.4 | 12.1 | 607 | 67 | |
| 2. | Sony A7R IV | Full Frame | 60.2 | 9504 | 6336 | 4K/30p | 26.0 | 14.8 | 3344 | 99 | |
| 3. | Canon G16 | 1/1.7 | 12.0 | 4000 | 3000 | 1080/60p | 21.0 | 11.7 | 230 | 54 | |
| 4. | Fujifilm X30 | 2/3 | 12.0 | 4000 | 3000 | 1080/60p | 20.4 | 11.2 | -312 | 49 | |
| 5. | Fujifilm X100T | APS-C | 16.0 | 4896 | 3264 | 1080/60p | 23.6 | 12.8 | 1483 | 78 | |
| 6. | Fujifilm X20 | 2/3 | 12.0 | 4000 | 3000 | 1080/60p | 20.1 | 10.9 | -462 | 46 | |
| 7. | Fujifilm X100S | APS-C | 16.0 | 4896 | 3264 | 1080/60p | 23.3 | 12.5 | 1329 | 75 | |
| 8. | Leica D-LUX 7 | Four Thirds | 16.8 | 4736 | 3552 | 4K/30p | 22.9 | 12.8 | 1002 | 72 | |
| 9. | Leica V-LUX Typ 114 | 1-inch | 20.0 | 5472 | 3648 | 4K/30p | 21.6 | 11.7 | 127 | 60 | |
| 10. | Leica X Typ 113 | APS-C | 16.1 | 4928 | 3264 | 1080/30p | 23.6 | 12.8 | 1491 | 78 | |
| 11. | Leica D-LUX 6 | 1/1.7 | 10.0 | 3648 | 2736 | 1080/60p | 19.8 | 10.8 | -303 | 43 | |
| 12. | Panasonic LX100 | Four Thirds | 12.7 | 4112 | 3088 | 4K/30p | 22.3 | 12.5 | 553 | 67 | |
| 13. | Sony A7R IVA | Full Frame | 60.2 | 9504 | 6336 | 4K/30p | 26.0 | 14.8 | 3344 | 99 | |
| 14. | Sony A7S III | Full Frame | 12.0 | 4240 | 2832 | 4K/120p | 23.7 | 13.9 | 2520 | 86 | |
| 15. | Sony A9 II | Full Frame | 24.0 | 6000 | 4000 | 4K/30p | 25.0 | 14.0 | 3434 | 93 | |
| 16. | Sony A7 III | Full Frame | 24.0 | 6000 | 4000 | 4K/30p | 25.0 | 14.7 | 3730 | 96 | |
| 17. | Sony A7R III | Full Frame | 42.2 | 7952 | 5304 | 4K/30p | 26.0 | 14.7 | 3523 | 100 | |
| Note: DXO values in italics represent estimates based on sensor size and age. | |||||||||||
Many modern cameras cannot only take still pictures, but also record videos. The two cameras under consideration both have sensors whose read-out speed is fast enough to capture moving pictures, and both provide the same movie specifications (4K/30p).
Feature comparison
Apart from body and sensor, cameras can and do differ across a variety of features. The two cameras under review are similar with respect to both having an electronic viewfinder. However, the one in the A7R IV offers a substantially higher resolution than the one in the D-LUX Typ 109 (5760k vs 2764k dots). The adjacent table lists some of the other core features of the Leica D-LUX Typ 109 and Sony A7R IV along with similar information for a selection of comparators.

| # | Camera Model |
Viewfinder (Type or 000 dots) |
Control Panel (yes/no) |
LCD Specifications (inch/000 dots) |
LCD Attach- ment |
Touch Screen (yes/no) |
Max Shutter Speed * |
Max Shutter Flaps * |
Built-in Flash (yes/no) |
Built-in Image Stab |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Leica D-LUX Typ 109 | 2764 | n | 3.0 / 921 | fixed | n | 1/4000s | 11.0/s | n | Y | |
| 2. | Sony A7R IV | 5760 | n | 3.0 / 1440 | tilting | Y | 1/8000s | 10.0/s | n | Y | |
| 3. | Canon G16 | optical | n | 3.0 / 922 | fixed | n | 1/4000s | 2.2/s | Y | Y | |
| 4. | Fujifilm X30 | 2360 | n | 3.0 / 920 | tilting | n | 1/4000s | 12.0/s | Y | Y | |
| 5. | Fujifilm X100T | 2360 | n | 3.0 / 1040 | fixed | n | 1/4000s | 6.0/s | Y | n | |
| 6. | Fujifilm X20 | optical | n | 2.8 / 460 | fixed | n | 1/4000s | 12.0/s | Y | Y | |
| 7. | Fujifilm X100S | 2360 | n | 2.8 / 460 | fixed | n | 1/4000s | 6.0/s | Y | n | |
| 8. | Leica D-LUX 7 | 2764 | n | 3.0 / 1240 | fixed | Y | 1/4000s | 11.0/s | n | Y | |
| 9. | Leica V-LUX Typ 114 | 2359 | n | 3.0 / 921 | swivel | n | 1/4000s | 12.0/s | Y | Y | |
| 10. | Leica X Typ 113 | optional | n | 3.0 / 920 | fixed | n | 1/2000s | 5.0/s | Y | n | |
| 11. | Leica D-LUX 6 | optional | n | 3.0 / 920 | fixed | n | 1/4000s | 11.0/s | Y | Y | |
| 12. | Panasonic LX100 | 2764 | n | 3.0 / 921 | fixed | n | 1/4000s | 11.0/s | n | Y | |
| 13. | Sony A7R IVA | 5760 | n | 3.0 / 2340 | tilting | Y | 1/8000s | 10.0/s | n | Y | |
| 14. | Sony A7S III | 9440 | n | 3.0 / 1440 | swivel | Y | 1/8000s | 10.0/s | n | Y | |
| 15. | Sony A9 II | 3686 | n | 3.0 / 1440 | tilting | Y | 1/8000s | 20.0/s | n | Y | |
| 16. | Sony A7 III | 2359 | n | 3.0 / 922 | tilting | Y | 1/8000s | 10.0/s | n | Y | |
| 17. | Sony A7R III | 3686 | n | 3.0 / 1440 | tilting | Y | 1/8000s | 10.0/s | n | Y | |
| Note: *) Information refers to the mechanical shutter, unless the camera only has an electronic one. | |||||||||||
One differentiating feature between the two cameras concerns the touch sensitivity of the rear screen. The A7R IV has a touchscreen, while the D-LUX Typ 109 has a conventional panel. Touch control can be particularly helpful, for example, for setting the focus point.
The reported shutter speed information refers to the use of the mechanical shutter. Yet, some cameras only have an electronic shutter, while others have an electronic shutter in addition to a mechanical one. In fact, both cameras under consideration feature an electronic shutter, which makes completely silent shooting possible. However, this mode is less suitable for photographing moving objects (risk of rolling shutter) or shooting under artificial light sources (risk of flickering).
The Leica D-LUX Typ 109 and the Sony A7R IV both have an intervalometer built-in. This enables the photographer to capture time lapse sequences, such as flower blooming, a sunset or moon rise, without purchasing an external camera trigger and related software.
Concerning the storage of imaging data, both the D-LUX Typ 109 and the A7R IV write their files to SDXC cards. The A7R IV features dual card slots, which can be very useful in case a memory card fails. In contrast, the D-LUX Typ 109 only has one slot. The A7R IV supports UHS-II cards (on both slots), while the D-LUX Typ 109 can use UHS-I cards.
Connectivity comparison
For some imaging applications, the extent to which a camera can communicate with its environment can be an important aspect in the camera decision process. The table below provides an overview of the connectivity of the Leica D-LUX (Typ 109) and Sony Alpha A7R IV and, in particular, the interfaces the cameras (and selected comparators) provide for accessory control and data transfer.

| # | Camera Model |
Hotshoe Port |
Internal Mic / Speaker |
Microphone Port |
Headphone Port |
HDMI Port |
USB Port |
WiFi Support |
NFC Support |
Bluetooth Support |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Leica D-LUX Typ 109 | Y | stereo / mono | - | - | micro | 2.0 | Y | Y | - | |
| 2. | Sony A7R IV | Y | stereo / mono | Y | Y | micro | 3.1 | Y | Y | Y | |
| 3. | Canon G16 | Y | stereo / mono | - | - | mini | 2.0 | Y | - | - | |
| 4. | Fujifilm X30 | Y | stereo / mono | - | - | micro | 2.0 | Y | - | - | |
| 5. | Fujifilm X100T | Y | stereo / mono | Y | - | micro | 2.0 | Y | - | - | |
| 6. | Fujifilm X20 | Y | stereo / mono | - | - | micro | 2.0 | - | - | - | |
| 7. | Fujifilm X100S | Y | stereo / mono | - | - | micro | 2.0 | - | - | - | |
| 8. | Leica D-LUX 7 | Y | stereo / mono | - | - | micro | 2.0 | Y | - | Y | |
| 9. | Leica V-LUX Typ 114 | Y | stereo / mono | Y | - | micro | 2.0 | Y | Y | - | |
| 10. | Leica X Typ 113 | Y | stereo / mono | - | - | mini | 2.0 | - | - | - | |
| 11. | Leica D-LUX 6 | Y | stereo / mono | - | - | mini | 2.0 | - | - | - | |
| 12. | Panasonic LX100 | Y | stereo / mono | - | - | micro | 2.0 | Y | Y | - | |
| 13. | Sony A7R IVA | Y | stereo / mono | Y | Y | micro | 3.2 | Y | Y | Y | |
| 14. | Sony A7S III | Y | stereo / mono | Y | Y | full | 3.2 | Y | - | Y | |
| 15. | Sony A9 II | Y | stereo / mono | Y | Y | micro | 3.1 | Y | Y | Y | |
| 16. | Sony A7 III | Y | stereo / mono | Y | Y | micro | 3.1 | Y | Y | Y | |
| 17. | Sony A7R III | Y | stereo / mono | Y | Y | micro | 3.1 | Y | Y | Y |
It is notable that the A7R IV has a microphone port, which can help to improve the quality of audio recordings by attaching an external microphone. The D-LUX Typ 109 does not feature such a mic input.
Studio photographers will appreciate that the Sony A7R IV (unlike the D-LUX Typ 109) features a PC Sync socket, so that professional strobe lights can be controlled by the camera.
Both the D-LUX Typ 109 and the A7R IV have been discontinued, but can regularly be found used on ebay. The D-LUX Typ 109 was replaced by the Leica D-LUX 7, while the A7R IV was followed by the Sony A7R V. Further information on the features and operation of the D-LUX Typ 109 and A7R IV can be found, respectively, in the Leica D-LUX Typ 109 Manual (free pdf) or the online Sony A7R IV Manual.
Review summary
So what conclusions can be drawn? Is there a clear favorite between the Leica D-LUX Typ 109 and the Sony A7R IV? Which camera is better? The listing below highlights the relative strengths of the two models.

Advantages of the Leica D-LUX (Typ 109):
- Better moiré control: Has an anti-alias filter to avoid artificial patterns to appear in images.
- Flexible image proportions: Has a multi-aspect sensor that allows for alternative image shapes.
- Ready to shoot: Has a lens built-in, whereas the A7R IV requires a separate lens.
- More compact: Is smaller (118x66mm vs 129x96mm) and thus needs less room in the bag.
- Less heavy: Is lighter even though it comes with a built-in lens (unlike the A7R IV).
- More prestigious: Has the Leica luxury appeal, which ensures a high resale price.
- More affordable: Was introduced at a lower price, despite coming with a built-in lens.
- More heavily discounted: Has been available for much longer (launched in September 2014).

Arguments in favor of the Sony Alpha A7R IV:
- More detail: Has more megapixels (60.2 vs 12.7MP), which boosts linear resolution by 122%.
- Maximized detail: Lacks an anti-alias filter to exploit the sensor's full resolution potential.
- High quality composites: Can combine several shots after pixel-shifting its sensor.
- Better image quality: Is equipped with a larger and more technologically advanced sensor.
- Richer colors: The sensor size advantage translates into images with better, more accurate colors.
- More dynamic range: Larger sensor captures a wider spectrum of light and dark details.
- Better low-light sensitivity: Larger sensor produces good images even in poorly lit environments.
- Better live-view autofocus: Features on-sensor phase-detection for more confident autofocus.
- Better sound: Can connect to an external microphone for higher quality sound recording.
- Better sound control: Has a headphone port that enables audio monitoring while recording.
- More detailed viewfinder: Has higher resolution electronic viewfinder (5760k vs 2764k dots).
- Larger viewfinder image: Features a viewfinder with a higher magnification (0.78x vs 0.70x).
- More detailed LCD: Has a higher resolution rear screen (1440k vs 921k dots).
- More flexible LCD: Has a tilting screen for odd-angle shots in landscape orientation.
- Fewer buttons to press: Has a touchscreen to facilitate handling and shooting adjustments.
- Faster shutter: Has higher mechanical shutter speed (1/8000s vs 1/4000s) to freeze action.
- More flexible: Takes interchangeable lenses and can thus be used with specialty optics.
- Longer lasting: Gets more shots (670 versus 300) out of a single battery charge.
- Easier travel charging: Can be conveniently charged via its USB port.
- Better sealing: Is splash and dust sealed for shooting in inclement weather conditions.
- Faster data transfer: Supports a more advanced USB protocol (3.1 vs 2.0).
- Easier wireless transfer: Supports Bluetooth for image sharing without cables.
- Better studio light control: Has a PC Sync socket to connect to professional strobe lights.
- Greater peace of mind: Features a second card slot as a backup in case of memory card failure.
- Faster buffer clearing: Supports a more advanced SD data transfer standard (UHS-II vs UHS-I).
- More modern: Reflects 4 years and 10 months of technical progress since the D-LUX Typ 109 launch.
If the number of relative strengths (bullet points above) is taken as a guide, the A7R IV is the clear winner of the contest (26 : 8 points). However, the relative importance of the various individual camera aspects will vary according to personal preferences and needs, so that you might like to apply corresponding weights to the particular features before making a decision on a new camera. A professional wildlife photographer will view the differences between cameras in a way that diverges from the perspective of a family photog, and a person interested in architecture has distinct needs from a sports shooter. Hence, the decision which camera is best and worth buying is often a very personal one.
How about other alternatives? Do the specifications of the Leica D-LUX Typ 109 and the Sony A7R IV place the cameras among the top in their class? Find out in the latest Best Travel-Zoom Camera and Best Mirrorless Interchangeable Lens Camera listings whether the two cameras rank among the cream of the crop.
In any case, while the specs-based evaluation of cameras can be instructive in revealing their potential as photographic tools, it remains partial and cannot reveal, for example, the shooting experience and imaging performance when actually working with the D-LUX Typ 109 or the A7R IV. User reviews, such as those found at amazon, can sometimes inform about these issues, but such feedback is often incomplete, inconsistent, and biased.
Expert reviews
This is where reviews by experts come in. The table below provides a synthesis of the camera assessments of some of the best known photo-gear review sites (amateurphotographer [AP], cameralabs [CL], digitalcameraworld [DCW], dpreview [DPR], ephotozine [EPZ], photographyblog [PB]). As can be seen, the professional reviewers agree in many cases on the quality of different cameras, but sometimes their assessments diverge, reinforcing the earlier point that a camera decision is often a very personal choice.

| # | Camera Model |
AP score |
CL score |
DCW score |
DPR score |
EPZ score |
PB score |
Camera Launch |
Launch Price (USD) |
Street Price |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Leica D-LUX Typ 109 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4.5/5 | 4.5/5 | Sep 2014 | 1,195 | ebay.com | |
| 2. | Sony A7R IV | 5/5 | + | 4.5/5 | 91/100 | 4.5/5 | 5/5 | Jul 2019 | 3,499 | ebay.com | |
| 3. | Canon G16 | 4/5 | + | .. | .. | 4.5/5 | 4.5/5 | Aug 2013 | 549 | ebay.com | |
| 4. | Fujifilm X30 | 4/5 | .. | .. | 76/100 | 4.5/5 | 4.5/5 | Aug 2014 | 599 | ebay.com | |
| 5. | Fujifilm X100T | 5/5 | + | .. | 81/100 | 4.5/5 | 5/5 | Sep 2014 | 1,299 | ebay.com | |
| 6. | Fujifilm X20 | 4/5 | + + | .. | 77/100 | 4.5/5 | 5/5 | Jan 2013 | 599 | ebay.com | |
| 7. | Fujifilm X100S | 5/5 | + + | .. | 81/100 | 4.5/5 | 5/5 | Jan 2013 | 1,299 | ebay.com | |
| 8. | Leica D-LUX 7 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4.5/5 | Nov 2018 | 1,195 | ebay.com | |
| 9. | Leica V-LUX Typ 114 | .. | .. | .. | .. | .. | 5/5 | Sep 2014 | 1,349 | ebay.com | |
| 10. | Leica X Typ 113 | 3.5/5 | .. | .. | .. | 3.5/5 | 4/5 | Sep 2014 | 2,295 | ebay.com | |
| 11. | Leica D-LUX 6 | .. | .. | .. | .. | 4/5 | 4/5 | Sep 2012 | 699 | ebay.com | |
| 12. | Panasonic LX100 | 5/5 | + + | .. | 85/100 | 5/5 | 5/5 | Sep 2014 | 899 | ebay.com | |
| 13. | Sony A7R IVA | 5/5 | + | 4.5/5 | 91/100 | 4.5/5 | 5/5 | Apr 2021 | 3,499 | amazon.com | |
| 14. | Sony A7S III | 4.5/5 | + + | 5/5 | 91/100 | 4.5/5 | 5/5 | Jul 2020 | 3,499 | amazon.com | |
| 15. | Sony A9 II | .. | .. | 5/5 | 90/100 | 5/5 | 5/5 | Oct 2019 | 4,499 | amazon.com | |
| 16. | Sony A7 III | .. | + + | 4.5/5 | 89/100 | 5/5 | 5/5 | Feb 2018 | 1,999 | amazon.com | |
| 17. | Sony A7R III | .. | + + | 4/5 | 90/100 | 4.5/5 | 5/5 | Oct 2017 | 3,199 | ebay.com | |
| Note: (+ +) highly recommended; (+) recommended; (o) reviewed; (..) not available. | |||||||||||
Care should be taken when interpreting the review scores above, though. The ratings were established in reference to similarly priced cameras that were available in the market at the time of the review. Hence, a score should always be seen in the context of the camera's market launch date and its price, and comparing ratings of very distinct cameras or ones that are far apart in terms of their release date have little meaning. Also, kindly note that some of the listed sites have over time developped their review approaches and their reporting style.

Check D-LUX Typ 109 offers at
ebay.com

Check A7R IV offers at
ebay.com
Other camera comparisons
Did this review help to inform your camera decision process? In case you are interested in seeing how other cameras pair up, just make your choice using the following search menu. As an alternative, you can also directly jump to any one of the listed comparisons that were previously generated by the CAM-parator tool.
- Canon G1 X vs Leica D-LUX Typ 109
- Canon SX620 vs Leica D-LUX Typ 109
- Canon T2i vs Leica D-LUX Typ 109
- Fujifilm X-E4 vs Leica D-LUX Typ 109
- Kodak AZ901 vs Sony A7R IV
- Leica D-LUX Typ 109 vs Nikon D3400
- Leica D-LUX Typ 109 vs Pentax K-3
- Leica V-LUX 3 vs Sony A7R IV
- Nikon D4 vs Sony A7R IV
- Nikon Z5 vs Sony A7R IV
- Nikon Zf vs Sony A7R IV
- Panasonic GX850 vs Sony A7R IV
Specifications: Leica D-LUX Typ 109 vs Sony A7R IV
Below is a side-by-side comparison of the specs of the two cameras to facilitate a quick review of their differences and common features.
| Camera Model | Leica D-LUX Typ 109 | Sony A7R IV |
|---|---|---|
| Camera Type | Fixed lens compact camera | Mirrorless system camera |
| Camera Lens | 24-75mm f/1.7-2.8 | Sony E mount lenses |
| Launch Date | September 2014 | July 2019 |
| Launch Price | USD 1,195 | USD 3,499 |
| Sensor Specs | Leica D-LUX Typ 109 | Sony A7R IV |
| Sensor Technology | CMOS | BSI-CMOS |
| Sensor Format | Four Thirds Sensor | Full Frame Sensor |
| Sensor Size | 15.7 x 11.8 mm | 35.7 x 23.8 mm |
| Sensor Area | 185.26 mm2 | 849.66 mm2 |
| Sensor Diagonal | 19.6 mm | 42.9 mm |
| Crop Factor | 2.0x | 1.0x |
| Sensor Resolution | 12.7 Megapixels | 60.2 Megapixels |
| Image Resolution | 4112 x 3088 pixels | 9504 x 6336 pixels |
| Pixel Pitch | 3.82 μm | 3.76 μm |
| Pixel Density | 6.85 MP/cm2 | 7.09 MP/cm2 |
| Moiré control | Anti-Alias filter | no AA filter |
| Movie Capability | 4K/30p Video | 4K/30p Video |
| ISO Setting | 200 - 12,500 ISO | 100 - 32,000 ISO |
| ISO Boost | 100 - 25,600 ISO | 50 - 102,400 ISO |
| DXO Sensor Quality (score) | .. | 99 |
| DXO Color Depth (bits) | .. | 26.0 |
| DXO Dynamic Range (EV) | .. | 14.8 |
| DXO Low Light (ISO) | .. | 3344 |
| Screen Specs | Leica D-LUX Typ 109 | Sony A7R IV |
| Viewfinder Type | Electronic viewfinder | Electronic viewfinder |
| Viewfinder Field of View | 100% | 100% |
| Viewfinder Magnification | 0.70x | 0.78x |
| Viewfinder Resolution | 2764k dots | 5760k dots |
| LCD Framing | Live View | Live View |
| Rear LCD Size | 3.0inch | 3.0inch |
| LCD Resolution | 921k dots | 1440k dots |
| LCD Attachment | Fixed screen | Tilting screen |
| Touch Input | no Touchscreen | Touchscreen |
| Shooting Specs | Leica D-LUX Typ 109 | Sony A7R IV |
| Focus System | Contrast-detect AF | On-Sensor Phase-detect |
| Manual Focusing Aid | Focus Peaking | Focus Peaking |
| Max Shutter Speed (mechanical) | 1/4000s | 1/8000s |
| Continuous Shooting | 11 shutter flaps/s | 10 shutter flaps/s |
| Electronic Shutter | up to 1/16000s | YES |
| Time-Lapse Photography | Intervalometer built-in | Intervalometer built-in |
| Image Stabilization | Lens-based stabilization | In-body stabilization |
| Fill Flash | no On-Board Flash | no On-Board Flash |
| Storage Medium | SDXC cards | SDXC cards |
| Single or Dual Card Slots | Single card slot | Dual card slots |
| UHS card support | UHS-I | Dual UHS-II |
| Connectivity Specs | Leica D-LUX Typ 109 | Sony A7R IV |
| External Flash | Hotshoe | Hotshoe |
| Studio Flash | no PC Sync | PC Sync socket |
| USB Connector | USB 2.0 | USB 3.1 |
| HDMI Port | micro HDMI | micro HDMI |
| Microphone Port | no MIC socket | External MIC port |
| Headphone Socket | no Headphone port | Headphone port |
| Wifi Support | Wifi built-in | Wifi built-in |
| Near-Field Communication | NFC built-in | NFC built-in |
| Bluetooth Support | no Bluetooth | Bluetooth built-in |
| Body Specs | Leica D-LUX Typ 109 | Sony A7R IV |
| Environmental Sealing | not weather sealed | Weathersealed body |
| Battery Type | Leica BP-DC15 | Sony NP-FZ100 |
| Battery Life (CIPA) | 300 shots per charge | 670 shots per charge |
| In-Camera Charging | no USB charging | USB charging |
| Body Dimensions |
118 x 66 x 55 mm (4.6 x 2.6 x 2.2 in) |
129 x 96 x 78 mm (5.1 x 3.8 x 3.1 in) |
| Camera Weight | 405 g (14.3 oz) | 665 g (23.5 oz) |

Check D-LUX Typ 109 offers at
ebay.com

Check A7R IV offers at
ebay.com
Did you notice an error on this page? If so, please get in touch, so that we can correct the information.

